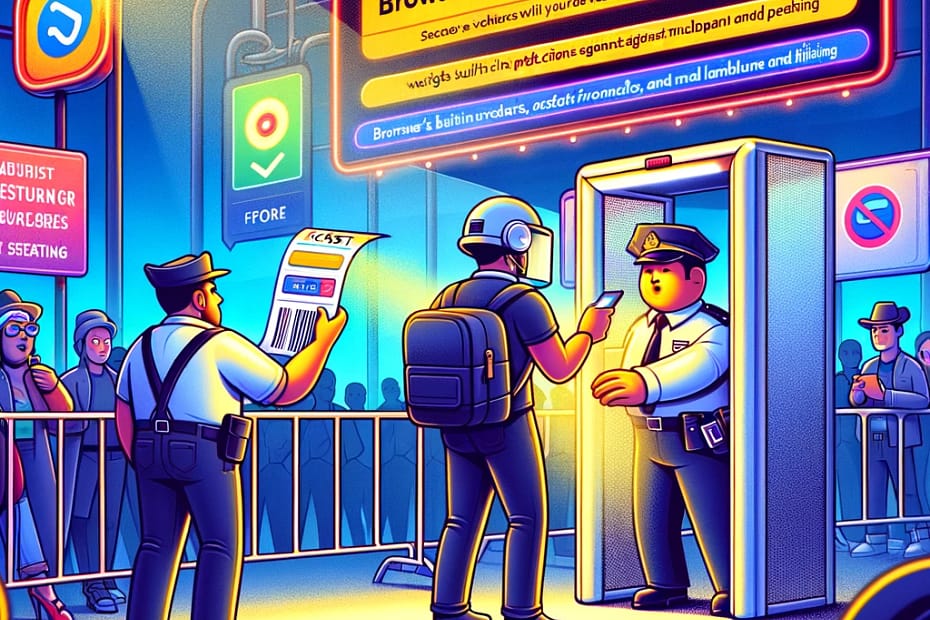
Browser security check explained
Imagine you’re trying to enter a super exclusive concert where they’re super cautious about who gets in. This concert is so exclusive, in fact, that even before you see the bouncer, there’s a smaller checkpoint that you have to pass through. That’s kind of like a browser security check when you’re surfing the web.
So, from your point of view, here’s what happens:
1. The Ticket Check (SSL/TLS Certificates)
First up, when you visit a website, your browser looks at the website’s “ticket” or SSL/TLS certificate. This is essentially the website’s way of proving that it is who it says it is, not some imposter trying to steal your info. If the certificate looks good, you’re allowed to move on. If it’s expired or just plain fishy, your browser will throw up a big warning, much like a bouncer flashing a “No Entry” sign.
2. The Pat Down (Browser’s Built-in Protections)
Next, your browser gives you a pat down for safety. It has built-in features to check for things like phishing or malware. If it senses something sketchy, it might block the site directly, warning you of potential harm, just as a security guard might stop someone with a suspicious item.
3. The VIP List (Updates and Patches)
Just like a concert venue often updates its security protocols, browsers receive updates that patch up any newfound security gaps. Staying updated means you’re keeping up with the latest security measures, ensuring that no sneaky tricksters find their way past your browser’s defenses.
4. The Secret Handshake (Cookies and Privacy Settings)
Your browser also manages a little secret handshake with each site you visit, often in the form of cookies. These cookies tell the site about your previous visits and can help load your preferences, making your experience smoother. However, just like in real life, you wouldn’t want everyone knowing everything about you, so your browser also lets you manage these settings to protect your privacy.
5. The Crowd Control (Cross-Site Tracking Protection)
Finally, modern browsers help control the crowd by limiting how much websites can track your movement from one site to another. This stops advertisers from knowing too much about your browsing habits, like a privacy fence keeping peeping toms at bay.
From your perspective, all these security measures are mostly happening behind the scenes, ensuring that your browsing experience is both safe and smooth, much like security at a concert working in the shadows to make sure the event goes off without a hitch. So next time your browser stops you at the door, it’s probably just doing its best to keep the party safe!
Image illustrating a browser security check envisioned as a concert entry scene! It visually represents various security measures as different aspects of getting into a concert, making the concept both engaging and easier to grasp.

So next time this message pops up… you know why!
Source OpenAI’s ChatGPT Language Model and DALLE – Images Picsart

Invest in your future & learn
Learn affiliate marketing & build your own website.
Heads up! Make sure you sign up using my referral link to get access to my personal coaching and all features.
👉 Sign Up